Delivering compute services over the Internet
Today we hear this term a lot in the IT industry which is referred to as a “Cloud”, so before we talk about cloud computing let us first understand what do we mean by "Cloud". Cloud can be defined as a global network of remote servers which are hooked together and are designed to store and manage data, run applications, or deliver content or a service.
So where are these servers located? I am sure that all of you have heard about Data Centers, so cloud providers have Data Centers and within these Data Centers lie these servers that provide you with compute resources like processor, memory, OS, applications etc.
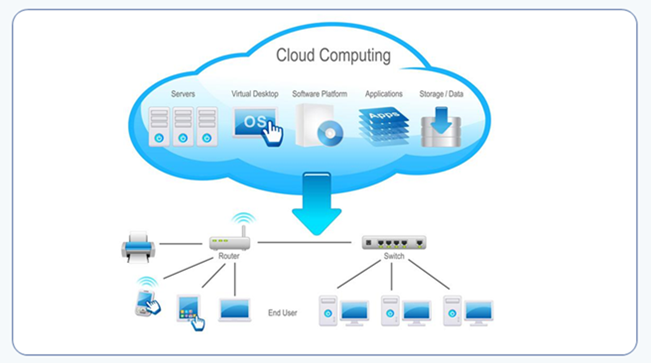
You also receive storage facilities to store your files and databases and you can access data securely from anywhere over the internet.
Cloud Providers
Cloud Providers like Microsoft, Amazon and Google to name a few basically provide you with Compute Power, Storage, Networking and other tools. It helps you analyze, secure, monitor and visualize your data and all these things together comprise of what we call as cloud computing.
So Cloud Computing is nothing but the delivery of all these services like Compute, Power, Storage, Networking and Analytic tools to you and you typically pay only for the cloud services that you use, its offered by the cloud providers as a pay as you go model.

What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
Some core benefits of the cloud computing are:
High availability
High availability means the application and its underlying systems in the cloud are available most of the time or we can say with very little downtime.
Fault tolerance
Fault tolerance means tolerant of faults, also referred normally as redundancy, so in cloud, if any component fails let’s say a power supply or a hard disk or a networking component there is always a backup component so that your services remain up and running.
Scalability
The resources in Cloud are scalable, which means you can add or remove resources as and when needed.
Elasticity
Cloud is elastic in nature, you can also use cloud to automatically add or remove the resources for you as per the demand.
Global Reach
Cloud services are available globally, i.e in different regions and around the globe.
Customer latency capabilities
If you are accessing a cloud service that is not local to you, you sometimes might experience it might lead to slowness or latency. Cloud providers have the ability to deploy resources in data centers around the globe thus addressing the issue.
Agility
Agility is the ability to react quickly. So you can allocate and de-allocate resources quickly in the cloud.
Predictive cost considerations
Before you go with a cloud your concern would also be about the cost, cloud providers also provide you with tools like calculators to predict what costs you will incur for a particular cloud service.
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery is the ability to recover from a disaster, Cloud service providers also provide you with Disaster Recovery solutions.
Security
Security is another concern you might have before you go with a cloud. To protect your data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats, Cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies, controls, and expert technology that can provide you with better security which might not be achievable by most of the organizations.
Economies of scale
Cloud providers run very large businesses and thus can purchase hardware at a much lower cost and thus they can pass this benefit to you as a customer. Also, you can avail discounts from cloud providers when you use bulk resources.
Consumption-based model
Cloud service providers operate on a consumption-based model, which means that you only pay for the resources that you use, also referred to as Pay as you go model. There is no upfront cost, no need to purchase costly infrastructure, you can simply sign up and start using the service. You can add and remove resources when you do not need them when you need remove them when not needed and you can also terminate the subscription when you no longer need them. You are only billed for what you use.
What are the different types of Cloud?
There are 3 types of cloud models:
- Public Cloud Model
- Private Cloud Model
- Hybrid Cloud Model
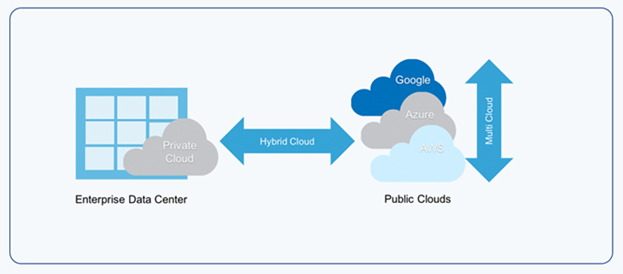
A Public Cloud is owned by the cloud services provider, you typically access Public Cloud securely over the internet, all you need is a subscription with the cloud provider, a device having a web browser and an internet connection. Eg. Microsoft, Amazon, Google etc.
A Private Cloud is owned, managed and operated by an Organization.
A Hybrid Cloud is a combination of Public Cloud with private or on-premises infrastructure.
What are the different types Cloud Services?
Cloud basically offers 3 types of services IAAS, PAAS and SAAS.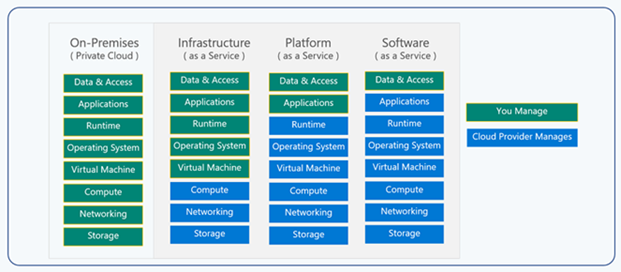
Infrastructure As a Service (IAAS)
When we say Infrastructure we are talking about- hardware, networking infrastructure, servers, virtual machines and Operating systems that are needed to run the applications in the cloud. So the Cloud service provider provides you with the infrastructure and you as a customer you are renting the infrastructure and pay only for the services that you use.
An eg. of IAAS would be creating a VM in the cloud and managing the VM.
Platform As a Service (PAAS)
Cloud provides you with a platform to build, test and deploy your applications. With Paas, you can quickly create and deploy your applications without worrying about managing the Virtual machines and Operating system on which it is running.
An eg. of PAAS would be creating a Web App or using a SQL Database.
Software As a Service (SaaS)
Software as service is a software that is hosted by the cloud provider and managed by the cloud provider. and As a customer you are just using the software on pay as you go basis and are not worried about managing the underlying infrastructure or the operating, you just pay for the software that you use.
An eg. of SAAS would be Office 365.
Hope this article helps you and gives you a good understanding of cloud computing.




















